Last Updated: 18 September 2022
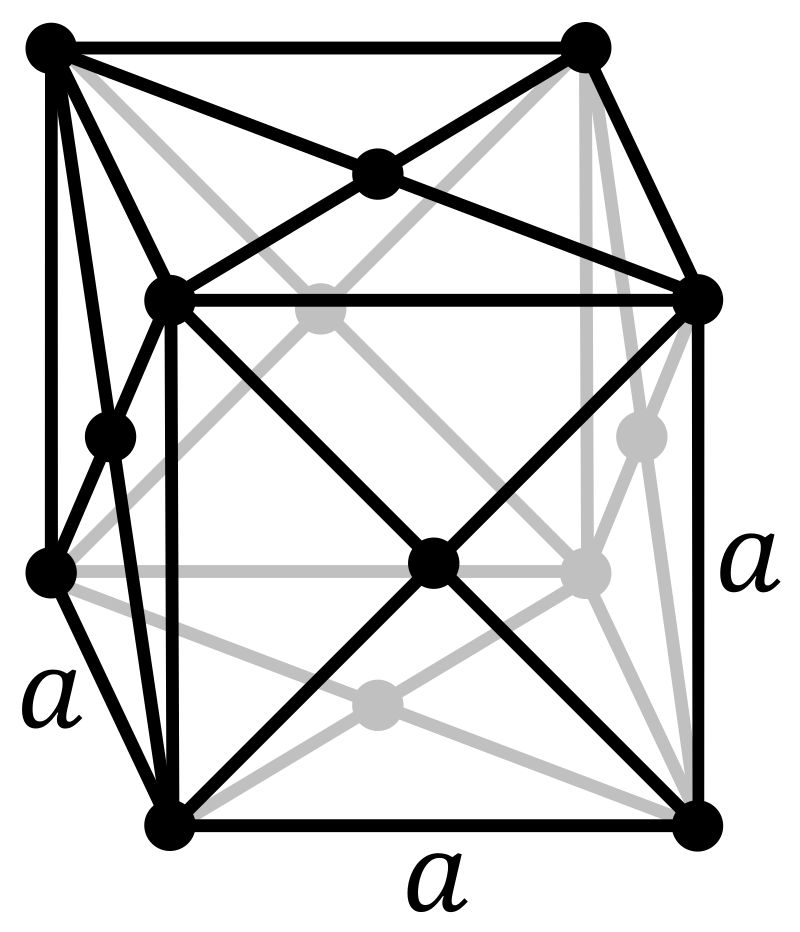
Figure 1. The crystal structure of Copper.
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu and atomic number 29. Like Iron and Chromium, Copper is an essential trace metal/mineral.
Copper is essential to all living organisms as a trace dietary mineral because it is a key constituent of the respiratory enzyme complex cytochrome c oxidase. In humans, Copper is found mainly in the liver, muscle, and bone. An adult human body contains between 1.4mg-2.1mg of copper per kg of body weight.
Copper plays an important role in many bodily functions. These include the production of red blood cells, regulation of heart rate and blood pressure, absorption of Iron, prevention of prostatitis (i.e. inflammation of the prostate), development and maintenance of bone, connective tissue, and organs like the brain and heart, and the activation of the immune system.
Copper-rich food sources include:
Typically, a daily value of less than 1mg of Copper is recommended for adult humans. Copper should not be ingested in excessive amounts as this would lead to Copper toxicity.
Sources and Citations:
* Please be advised: always seek medical consultation if you require medical help or attention. The contents of this Codex are for educational purposes and are not intended to offer personal medical advice.