Last Updated: 19 September 2022
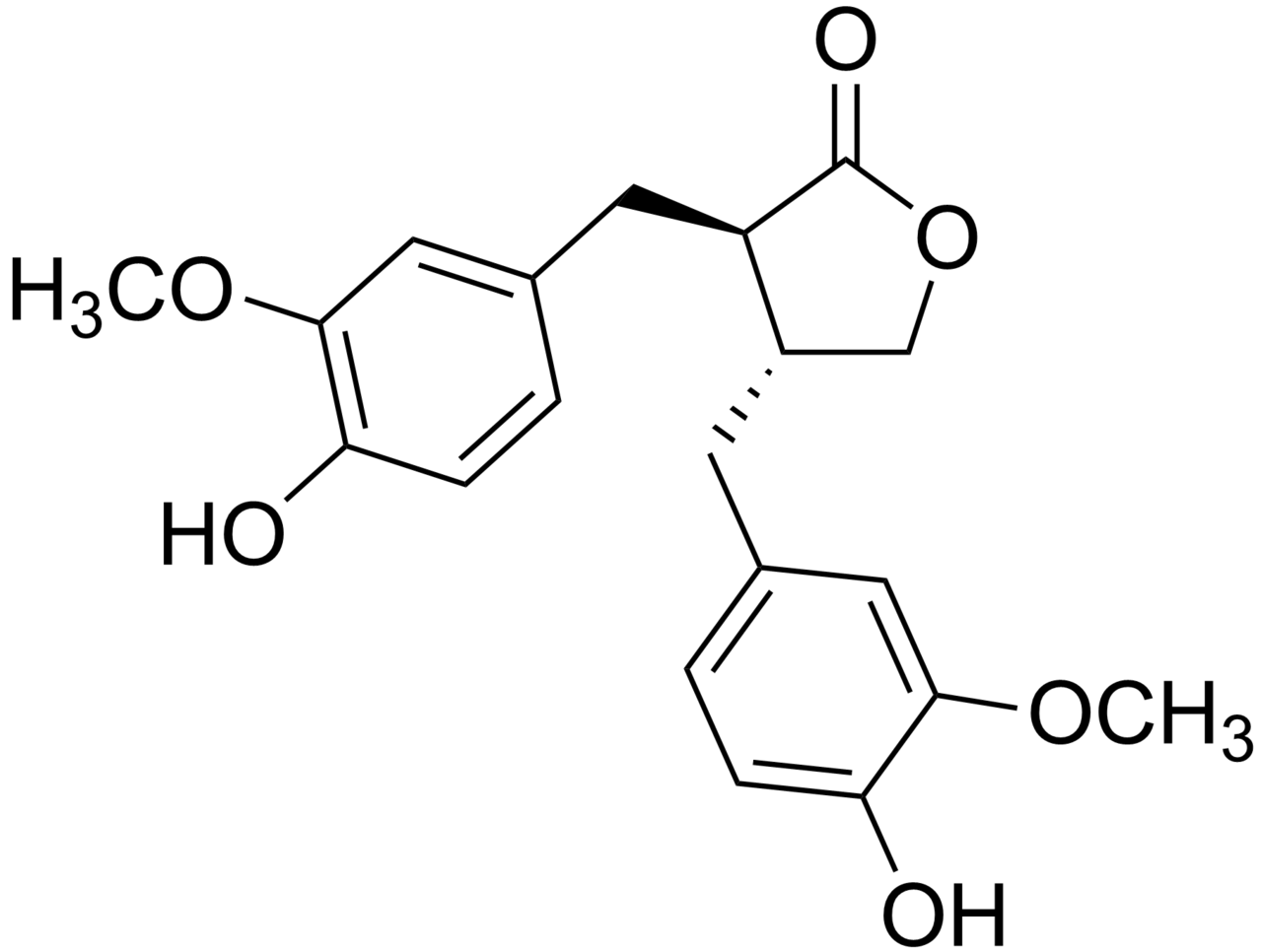
Figure 1. The chemical structure of Matairesinol, a type of Lignan.
Lignans are a large group of low molecular weight polyphenols found in plants, particularly in seeds, whole grains, and vegetables. Lignans are soluble in water and are metabolised by gut microflora in mammals into compounds called enterolignans. Lignans are also precursors to phytoestrogens.
Lignans can be obtained from food sources such as flaxseeds, sesame seeds, rye, wheat, oat, barley, soybeans, tofu, cauliflower, cabbage, kale, garden cress, bok choy, broccoli, Brussels sprouts, mustard plant, apricots, and strawberries. Lignans are not found in seed oil.
As a dietary supplement, Lignans are often promoted as an antioxidant (due to enterolignans), a cardioprotective compound (due to phytoestrogens, which exhibit pseudo-estrogenic effects in the body), dietary fiber, and anti-inflammatory effects. Health benefits attributed to Lignans include a lowered risk of heart disease, menopausal symptoms, osteoporosis, and breast cancer.
Sources and Citations:
* Please be advised: always seek medical consultation if you require medical help or attention. The contents of this Codex are for educational purposes and are not intended to offer personal medical advice.